AI is a tool to amplify how we design for better user experiences

Ever since ChatGPT started making headlines, there have also been warnings for people in all types of fields that AI is coming for their jobs. It’s true that AI is a threat in some ways and will likely take over tasks that have traditionally been done by designers. But that doesn’t mean AI will completely take over design.
AI will enhance user experience (UX) designers’ jobs. Designers will need to learn how to leverage AI as another essential tool, like Figma or Sketch. But more than that, designers will also need to learn how to design experiences that use AI, because that’s what users will need and come to expect.
In this article we’ll explore how AI and UX work together, where designers should use AI, and what experiences already use it that designers need to consider.
First, let’s define AI
AI — short for artificial intelligence — is a very broad term for building technology to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. The idea is to build “smart” machines. These machines model and then improve upon the human mind’s capabilities.
AI is not new. According to reports, the worldwide market for AI was estimated at $119.78 billion(B) in 2022. The market is predicted to grow exponentially.
Thanks to advancements in machine learning and deep learning, we’re seeing a profound shift in what AI can accomplish. AI is already built into many tech products we use everyday, from Google docs making suggestions as you write to voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa.
Microsoft’s use of AI in Bing and ChatGPT are the latest in a long history of AI in technology. Today, technological advances and awareness have made it more visible.
The benefits of using AI in UX Design
UX design already determines how users interact with a product and their overall satisfaction with it. What will change is how tightly AI integrates with UX. It will become increasingly important as a tool to design for.
Here are some examples of how designers can use AI to improve the user experience.
To identify patterns
By analyzing data on user interactions with a product, AI algorithms can identify patterns and make predictions about user behavior. This information can then be used to personalize the user experience, making it more tailored to the user’s individual needs and preferences. For example, product designers could use AI to create a recommendation system that suggests products or content that a user is likely to be interested in, based on their past behavior.
Netflix does this when it recommends “Top Picks” — a list of shows and movies based on previous content the user has watched or liked.

To improve efficiency and automation
Another important benefit of using AI in UX design is improved efficiency. Intelligent automation not only has benefits for the end consumer, but also for businesses that can decrease costs through finding inefficiencies and making improvements.
One example is using chatbots to interact with customers. Chatbots that use AI can answer questions, make recommendations, make appointments, and even take payments. Sephora uses a chatbot to provide beauty recommendations.

AI use cases are more than chatbots, though. Just about every business unit can use AI to improve efficiency. Sales may use AI tools for lead generation and network matchmaking, while legal departments may use AI to uncover fraud.
To enhance accessibility
AI can also enhance the accessibility of digital products. For example, AI-powered voice recognition systems can make it easier for users with disabilities to interact with digital products.
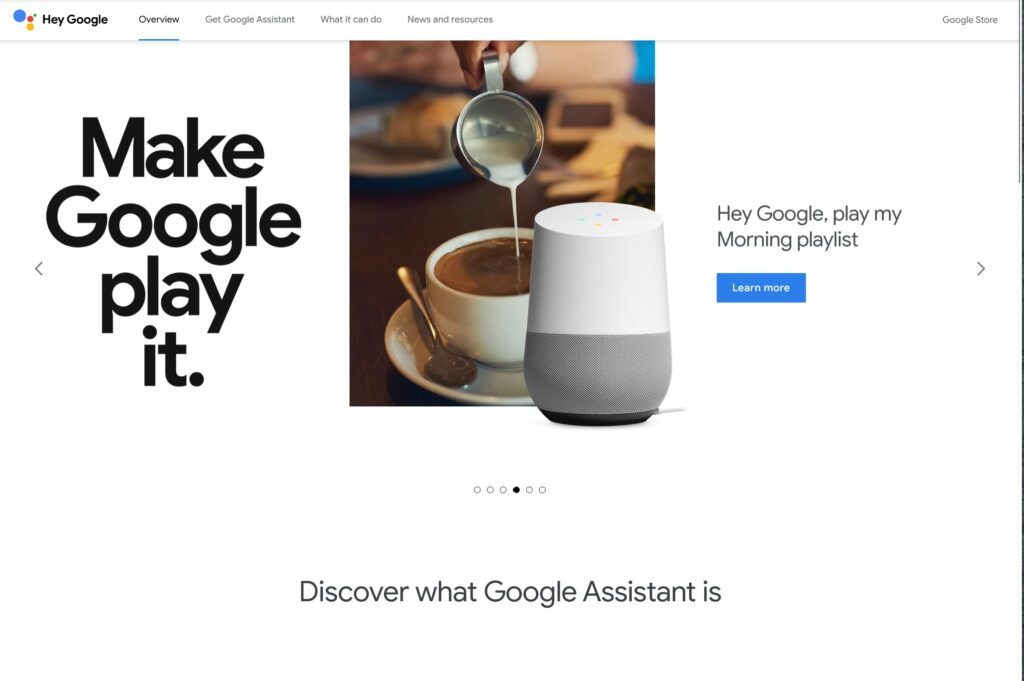
Here’s how it works. Instead of only being able to type, users can speak, and the tool transcribes what the user says into text. Google Assistant is a great example. The tool allows you to speak a command, like to send a text message or play a song. Voice assistants are accessible to all types of users.
AI can also employ image recognition. This can enhance the accessibility of digital products for users with disabilities, such as those who are visually impaired, by providing a description of the image, even if one was not initially provided.
AI in the UX Process
AI not only can help end users, but it can also help designers be more efficient in their roles. Over the next few years, we can expect to see more tools enter the market designed to help designers and researchers do their work.
For example, on the research side, some tools are automating the recruiting process by creating synthetic users — no humans needed. There are also tools to improve usability testing. For example, one tool predicts behavior based on heat maps.
For designers, there are products to help create images, mockups, and copywriting. And more tools are likely on the way. The trick is — how to decide?
How to choose the right AI technology for a UX project
With so many AI technologies available, choosing the right one for a UX project can be challenging.
For designers and researchers choosing AI to improve their own processes, I recommend trying them out one by one. Many products offer demos and trials to see how they work. Trying out the tools is a great way to see its potential and determine whether or not it will speed up your work or provide any other value.
Another consideration is cost. Many of the current products available now come with a subscription. Subscriptions can add up, so it’s best to think about how much value the tool will offer you in the long run.
In terms of thinking about how AI tools can be integrated into the final product, start with these five steps.
Remember the user needs
When choosing an AI technology for a UX project, it is important to start with user needs. This includes understanding their goals, motivations, and pain points, as well as the context in which they will be using the product. The right AI technology should be aligned with user needs and should enhance the UX in a meaningful way.
Consider the technical requirements
The next consideration should be the technical requirements of the project. This includes the type of data that will be used to train AI algorithms, the computational resources required, and the complexity of the algorithms needed. It is important to choose an AI technology that can handle the technical requirements of the project, while also being feasible to implement and integrate into the product.
Consider the data availability and quality
Data is the fuel that powers AI algorithms, so it is important to consider the availability and quality of data when choosing an AI technology. If the data is not available or is of poor quality, the AI algorithms will not perform as well, resulting in a subpar experience. It is important to choose an AI technology that can work with the available data and that can improve the quality of the data over time.
Consider cost and scalability
Finally, it is important to consider the cost and scalability of AI technology. This includes the cost of implementing and integrating the technology into the product, as well as the cost of maintaining and updating it over time. It is also important to consider whether the AI technology is scalable and can accommodate future growth and expansion.
Consider ethical and privacy implications
When choosing an AI technology, it’s also important to consider ethical and privacy implications. This includes considering the potential for bias and discrimination, as well as ensuring that user data is securely stored and protected. You should choose an AI technology that is aligned with your organization’s principles, local laws, and one that can be trusted by users.
Ensuring ethical and inclusive design when using AI
Consider bias and discrimination
One of my key concerns with AI is its potential for bias and discrimination. AI algorithms are trained on data. So the question is — how good is the source data? If the source data is biased, the algorithms will reflect this bias. This can result in discriminatory experiences for users. To ensure ethical and inclusive design when using AI, it’s critical to consider the potential for bias and discrimination and to take steps to mitigate these risks.
Ensure privacy and data security
For intelligent automation to work, user data is collected, stored, and processed. How well will the data be protected. Will its be used in an ethical or unethical manner? Always ask if and how user data is stored securely. And think about whether users have control over their data and who it is shared with.
Involve diverse stakeholders
Including diverse stakeholders in the design process will help ensure inclusivity. Diversity includes individuals from different backgrounds, perspectives, and experiences, as well as experts in ethics, privacy, and inclusivity. By involving a diverse range of stakeholders, organizations are taking steps to make sure the use of AI is inclusive and equitable.
I wrote about the importance of diversity in design teams. You can read that article on avoiding unintended consequences in design here.
Continuously monitor and evaluate
Finally, it’s important to continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of AI on users. This includes regularly reviewing and updating AI algorithms to ensure they are fair and unbiased, as well as conducting user research to understand the impact of AI on the user experience.
Downsides of using AI in UX design
While AI can improve the user experience, it definitely has its challenges and limitations. In addition to ethical concerns, AI also has other downsides to consider.
Lack of creativity and flexibility
One of the biggest downsides of using AI in UX design is the potential loss of creativity and flexibility. AI algorithms can automate certain tasks, but they cannot replace the creativity and intuition of human designers. This can limit the ability to create unique and innovative designs that meet the needs of users.
Bias and discrimination
As I mentioned above, AI has the potential for bias and discrimination. AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. For example, facial recognition algorithms have been shown to be biased against people with darker skin tones, resulting in lower accuracy rates. The 2018 “Gender Shades” project found facial recognition algorithms have poor accuracy for young, black women, between 18 and 30 years old.

Technical limitations
AI algorithms can only perform as well as the data they are trained on and the quality of the algorithms themselves. This means that if the data is poor quality or the algorithms are poorly designed, it can result in inaccurate or poor results.
Let’s face it, AI just isn’t there quite yet. If you’re like me and still struggle to figure out how to ask Amazon’s Alexa to play a specific song without repeating yourself 15 times, then you understand. AI has come a long way, but natural language processing isn’t the same — yet — as natural conversation. You have to speak exactly what the computer needs you to speak and you can’t interrupt it. It’s not the same as having a human conversation.
Cost and resource requirements
Developing and training AI algorithms requires a significant investment of time and resources, and not all organizations have the resources to invest in these technologies. Ongoing maintenance and improvement of AI algorithms can also be costly.
Privacy concerns
Finally, the use of AI in UX design can raise privacy concerns. AI algorithms require access to large amounts of data to provide insights into user behavior and preferences. This data can be sensitive and personal, and if it is not properly secured, it can lead to privacy breaches and violations.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to greatly improve the UX of digital products, though not without its challenges and limitations. But with the right steps and planning, UX designers can leverage AI as a tool for themselves as well as users. To do this, they should
- Start with a clear understanding of user needs
- Identify opportunities for AI
- Plan and design with AI in mind
- Consider the downsides
- Take steps to mitigate the risks
By addressing these challenges and limitations, organizations can ensure that they are using AI technologies in a way that benefits users and enhances the UX of digital products.
*The author used ChatGPT to outline this article; however, the author researched, verified, wrote, and edited the article.











